Stopping distances for
cars
Many drivers have a false belief that if the car in front starts braking they can react, brake and come to a stop, still leaving the same distance between the two vehicles.
The total stopping distance of your vehicle depends on four things:
- your perception time,
- your reaction time,
- your vehicle reaction
time, and
- your vehicle braking
capability.
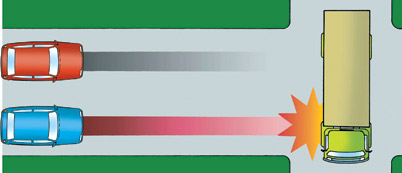
Your perception time is how long you take to see a hazard and your brain realising it is a hazard requiring you to take immediate action. This can be as long as 1/4 to 1/2 of a second.
Your reaction time is how long you take to move your foot from the accelerator to the brake pedal once your brain understands you are in danger. Your reaction time can vary from 1/4 to 3/4 of a second.
These first 2 components of stopping distance are down to you and can be affected by alcohol, drugs, tiredness, fatigue or lack of concentration. A perception and reaction time of 4 seconds at 100 km/h means the car travels 110 metres before the brakes are applied (this is more than the length of a football pitch).
Once you apply the brake pedal it will take time for your vehicle to react. This depends on the condition your vehicle is in and, in particular, the condition of the braking system.
The last factor that determines your total stopping distance is the vehicle's braking capability. This depends on many things, for example:
- brakes,
- tyre pressure, tread and
grip,
- the weight of the
vehicle,
- the vehicle's
suspension, and
- road surface.
|
Table 1: Stopping distance under dry conditions |
|||
|
Speed (km/h) |
Reaction distance (m) |
Braking distance (m) |
Total stoppingg distance (m) |
|
|
5.5 |
5.3 |
10.8 |
|
|
9.2 |
14.8 |
24.0 |
|
|
11.0 |
21.4 |
32.4 |
|
|
14.7 |
38.0 |
52.7 |
|
|
18.3 |
59.4 |
77.7 |
|
|
22 |
85.5 |
107.5 |
Source Transport Research Laboratory, UK, 2007, © Road Safety Authority, 2007
|
Table 2: Stopping distance under wet conditions |
|||
|
Speed (km/h) |
Reaction distance (m) |
Braking distance (m) |
Total stoppingg distance (m) |
|
|
5.5 |
9.4 |
14.9 |
|
|
9.2 |
26.1 |
35.2 |
|
|
11.0 |
37.5 |
48.5 |
|
|
14.7 |
66.7 |
81.4 |
|
|
18.3 |
104.3 |
122.6 |
|
|
22 |
150.2 |
172.2 |
Source Transport Research Laboratory, UK, 2007, © Road Safety Authority, 2007
It is worth noting that from 50km/h to 100km/h the total braking distance of your car can increase from 15 metres to 60 metres. When you double the speed of your car you multiply the total braking distance four times.
Remember a 5km/h difference in your speed could be the difference between life and death for a vulnerable road user like a pedestrian.
- Hit by a car at 60km/h,
9 out of 10 pedestrians will be killed.
- Hit by a car at 50km/h,
5 out of 10 of pedestrians will be killed.
- Hit by a car at 30km/h,
1 out of 10 pedestrians will be killed.
Source RoSPA UK

Source Transport Research Laboratory, UK, 2007, © Road Safety Authority, 2007
Skidding
Any factor which reduces the grip of your tyres on the road is a possible source of skidding. Wet or greasy roads, overloading, worn or improperly inflated tyres, mud, leaves, ice, snow, harsh acceleration, sudden braking, or excessive speed for the conditions can all cause or contribute to a skid.
Aquaplaning occurs when a car is being driven on a wet road and a film of water builds up between the tyres and the road surface.
When that happens, the car loses contact with the road, and braking and steering is affected.